Newspapers
Newspapers are very important and integral part of any library or information centre. No library can imagine without the existence of any type of newspaper. Be it any type of academic library or any other special learning and knowledge centre, newspaper always available to greet their patron.
As nature, Newspapers are the very prominent type of periodical publication gives up to date news, articles in general and also related to a specific topic, subject, place etc. if these are not specified Normally they are published on daily basis. But sometimes the periodicity may vary from twice a day to bi-monthly or monthly.
Origin of Newspaper can be traced in Germany in near about 1400 when open handwritten newsletters were circulated.
During Renaissance, these newsletters were used to update the merchants about war and custom related news and information. With the advent of printing technology, these hand-written pamphlets replaced by printed newsletters. In 16 the century, first newspaper was published in the name of The Weekly News and this was the beginning of newspaper era.

In India, Calcutta is the city where the first newspaper was published in 1780 by James Augustus Hickey with the name, Bengal Gazette and with this new wave has started. With the amalgamation of information technology with information, newspaper technology has also seen the sea change. E-Version of printed newspaper is a daily routine for everyday life.
E-newspaper
1970 was the year when the electronic version of printed newspaper came in light. That was the time when e-paper was just content based e-version of their counterpart. Within 20 years, roughly 10 newspapers were in electronically circulation mode. But with the emerging information technology, e-newspapers also increased rapidly in numbers and with the passing of 2001, world wide web as ready to host more than 3400 electronic newspapers. Web2 technology has also touched the e-newspaper technology. With this e-paper is more interactive and now a reader can interact with newspaper team in forum, comment section and chat room etc.
Within 20 years, roughly 10 newspapers were in electronically circulation mode. But with the emerging information technology, e-newspapers also increased rapidly in numbers and with the passing of 2001, world wide web as ready to host more than 3400 electronic newspapers. Web2 technology has also touched the e-newspaper technology. With this e-paper is more interactive and now a reader can interact with newspaper team in forum, comment section and chat room etc.
With the dawn of twenty first century, e-newspaper also became integral- part of daily life across the globe. Every second household is enjoying newspaper on their tablet, mobile or any type of communication tool with their own convenience time and availability. Continuous up-dation of news, events of all concerned areas not an issue with the readers.
There are immeasurable e-newspapers are available to explore across the globe. I have tried to the summarised list of available e-paper in the virtual world and waiting to explore:
- onlineNewspaper.com
- Newspaper US and Worldwide
- World Newspaper and Magazine Online
- Newspapers & Magazines
- Newspaper US and Worldwide
- World Newspapers and Magazines Online
- Newspaper Map
- World Newspaper and Magazines
- Press Display
- World Newspaper.com
- NEWSEUM
- Newspaper Index.com
- The Economist
- The Independent
- COMSCORE
- All Newspapers
- DMOZ
- Global Newspaper
- The Guardian
- News Link
- Easy Newspaper
- One World Nation Online
- Global Times
- Indekx
- List of Newspapers
- Hindustan times
Range of Information Resources
Information Resources:
There are number of information resources required and available in any academic library. What kind of information resources should be subscribed, Generally it depends upon the nature of clientele for whom library has to establish. Here I have tried to present the table devised by Hanson and Grogan for a common list of Information resources suitable for any type of academic library, ranging from primary to college or research library. These information resources are classified as per their information characteristics.
Primary Information Resources are those which contains and provides first hand information in regard of any thing, event, organisation or any living being. In this sense, these documents can be known for providing new interpretation of any existing knowledge from universe of wisdom.
Secondary Information Resources act as guiding tool to get the first hand information resources, i.e. Primary Information Resources. Generally, these resources do not carry any original or primary type information, infect these are the compilation of varied information of different primary resources.
Tertiary Information Resources can be categorised list or index of Secondary Information Resources. The main function of these resources is to facilitate researchers to find out their relevant information in minimum time and in order to that they are fulfilling the fourth law of the library science which advocates to save the time of reader.
|
Primary |
Secondary |
Tertiary
|
| 1.Periodicals | 1. Bibliographies | 1.Yearbooks |
| 2.Research and Technical
Reports |
||
| 3.Conference Proceedings | 2. Indexing and Abstracting Services | 2.Directories |
| 4.Official Publications | ||
| 5.Patents | 3. Reviews, State of the art reports Progress
Advances Monographs |
3.Bibliography of Bibliographies |
| 6.Standards | ||
| 7.Trade Literature | 4. Reference Books
Encyclopedia Handbooks Tables Formulation |
4.List of research in progress |
| 8.Theses and Dissertations | 5. Text Books | 5.Guide to Information Sources and Organisations |
| 9.Laboratory Notebooks | ||
| 10.Diaries | ||
| 11.Internet Research Reports | ||
| 12.Correspondences, Personal Files |
New TimesMachine from the Gray Lady
New TimesMachine from the Gray Lady
An aptly named “TimesMachine” from The New York Times offers up online images of historic newspapers from the 1850s through the 1920s. You can view sample papers at http://timesmachine.nytimes.com/browser, but to browse through the 70-year spread of history you need to be a home delivery subscriber of the paper
Besides the boon to students and history buffs alike, the new site gets my gears going about the online media business and the huge promise afforded by services like Amazon’s S3.
That’s because while I agree with Silicon Alley Insider that the offering won’t be a ‘huge money-maker’ for the Times, it doesn’t have to be. From what NYT engineer Derek Gottfrid describes, once the papers were all digitized he was able to use Amazon’s web services to quickly get the rest of the work done.
In a video interview with Robert Scoble, Gottfrid says “Once we moved it up to Amazon for a couple hundred dollars… we were able to do it in about 24-36 hours… It was a great use of Amazon for us to be able to churn through the data.”
Gottfrid doesn’t specifically describe how he used Amazon’s services, and I don’t want to give Amazon too much free advertising here. But this seems like more justification of my high hopes for the new platforms afforded to enterprising developers, whether they’re at resource-starved companies or in their own living room, for getting great stuff up online.
Along with Amazon, Google is also jumping into this space. I previously wrote about its App Engine Platform, which likewise aims to allow anyone with a great idea to bring it to life online.
This article publishes in The New York Times . The New York Times is a daily newspaper published in New York City and distributed internationally. It is owned by The New York Times Company, which publishes 15 other newspapers, including the International Herald Tribune and The Boston Globe. It is the largest metropolitan newspaper in the United States.
On 24 May 2008 it has announced the back issue newspapers from Sept 22, 1851 to Dec 30, 1922 as online version. But these are not on open access because to access these issues one has to subscribe the Home Delivery service of this newspaper.
The Home delivery Service is paid service available for within and outside New York inhabitants.
Important link
http://timesmachine.nytimes.com/browser
LIS News across the globe
BUBUL is a powerful gateway in the area of Library and Information world. This is the link which gives us the details of forthcoming LIS Conferences across the globe. These conferences are arranged on monthly basis.
Information Science Conferences Worldwide
Library Automation
Preamble
1940 was the time when libraries have seen semi-mechanical applications in libraries and with this Library Automation process were initiated. These applications were found in the form of edge-notched cards, optical coincidence, and peek-a-boo cards etc. with this the library automation journey was started and punched cards, data processing units, first generation computers CD-Roms, Optical Disks and now with the information explosion use of Internet are few tools have been using by Information manages to ease out routing process in and around library.
History
1940 was the time when libraries have seen semi-mechanical applications in libraries and with this Library Automation process were initiated. These applications were found in the form of edge-notched cards, optical coincidence, and peek-a-boo cards etc. with this the library automation journey was started and punched cards, data processing units, first generation computers CD-Roms, Optical Disks and now with the information explosion use of Internet are few tools have been using by Information manages to ease out routing process in and around library.
The term ‘Automation’ was coined initially by Dr. D.S. Harder in 1936. In the words of Dr. Harder, “Automation is the automatic handling of parts between progressive production processes in relation to engineering industries”. Actually, the origin of Automation word can be seen from the Greek word, ‘Automose’ which means anything carries the power of spontaneous motion or self-movement.
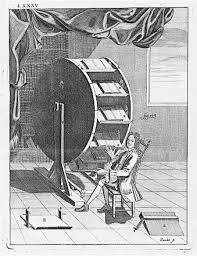
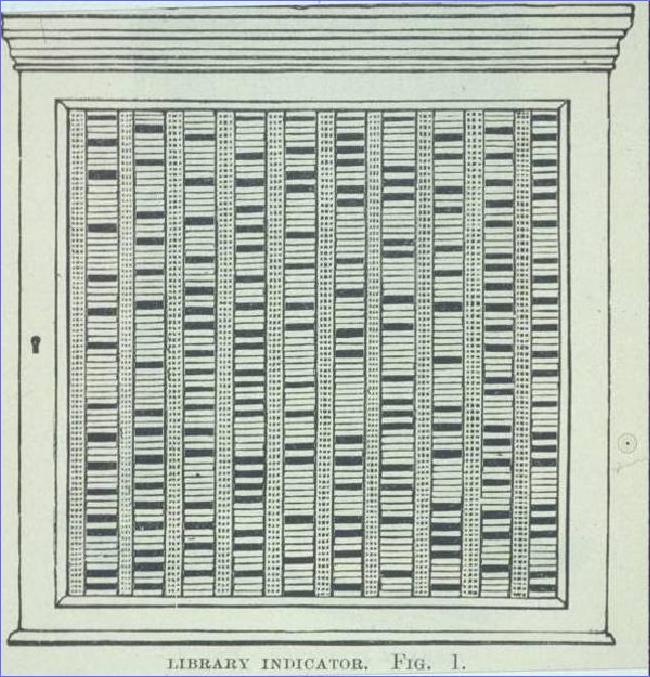
With the amalgamation of Information Technology in the library environment, slowly and gradually, library manual activities also replaced by computerised form. But if we see the history, way back in 1588, in France, there was a BOOK WHEEL available for library readers. With the help of a paddle of this instrument, readers turn their reading table. After passing of two and half centuries, in 1863, another model of Library Automation can be seen in the form of ‘Book Indicator’. In order to facilitate the circulation desk activities, this instrument was devised by Albert Cotgreave. With the help of miniature books, this instrument shows the status of books in the library, i.e. whether the book is on the shelf, issued or overdue.
But these are not alone instances of Library Automation, there are countless more which are not recorded in books.
Library Automation history shown officially work started in somewhere in 1930 with the invention of Punched Card system. With the beginning of 1940s, computer system started to use for automation of various library operations. The library automation journey got major kick-start when some special libraries of USA started automation of library house-keeping activities. Furthermore with the availability of microcomputers in libraries in 1980s, the library automation process proceeded at the speed of rocket.
|
|


